A cloud deployment model is a specific configuration of environmental parameters such as accessibility and proprietorship of the deployment infrastructure and storage size. It is defined according to where the infrastructure for the deployment resides and who has control over it.
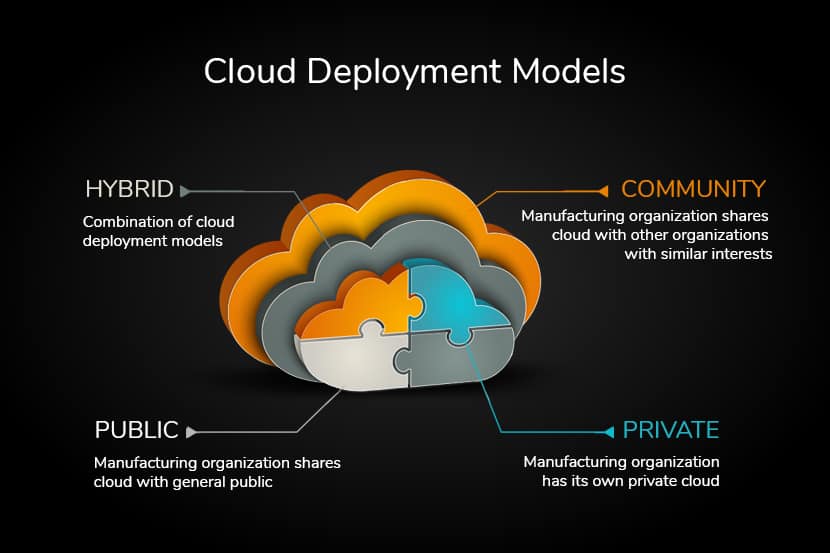
Over the years, with the rise in demand for cloud computing, the need for cloud deployment models has also increased. So, there are a total of 4 cloud deployment models – Public, Private, Community, and Hybrid. And while all of these models are based on similar technology, each of them varies in scalability, cost, performance, and privacy. With all the different models satisfying different needs of your organization, we’re presenting some of the key factors of the 4 different deployment models to give you a clear picture of what each one of them has to offer.
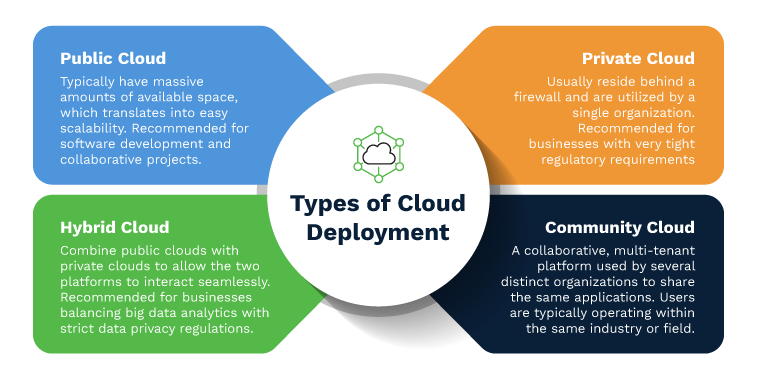
Public Cloud Deployment
While the name speaks for itself, a public cloud is a cloud where services are rendered by third-party providers over an open network for public use. Yes. It’s available to the general public and data is created & stored on third-party servers. The public cloud deployment model is one of the most commonly used cloud services. It’s a popular option for apps, file sharing, and insensitive data storage.
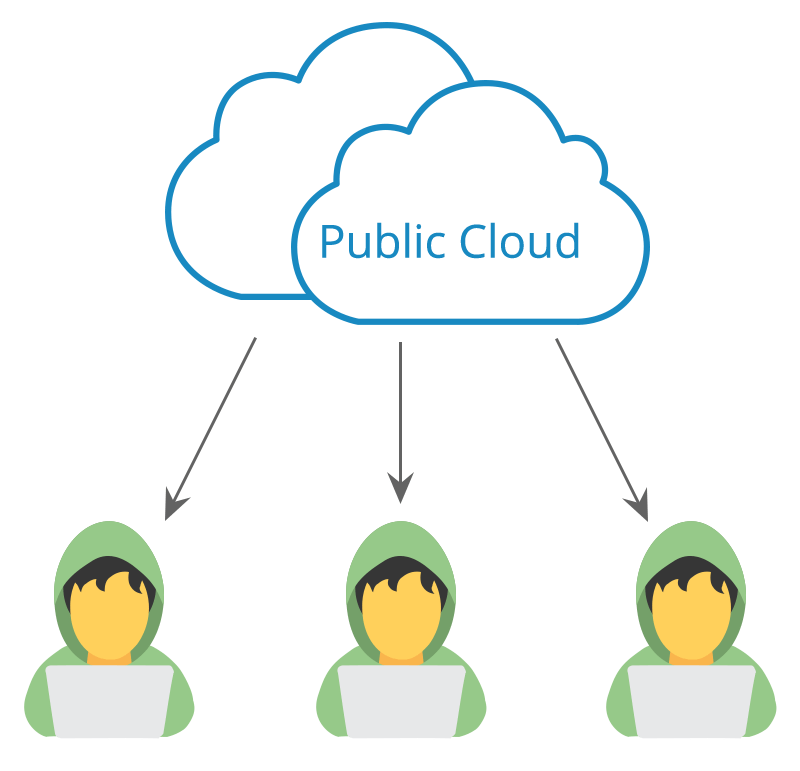
Under this model, the service provider owns and operates all the hardware that is needed to run a public cloud. They keep devices in massive data centers. This model also plays a vital role in development and testing. That’s because it’s cheap, easily configurable, can be deployed quickly, and supports fluctuating demands.
Advantages
• Low Cost – The service providers are the ones who fund the entire infrastructure (no need for you to invest in hardware or software). And aside from the initial fee, you’re good to go on the ‘pay per use’ policy under this model, which means, no overhead costs.
• Convenient Infrastructure Management – You don’t need to develop or maintain your software because the service provider does that for you. The setup and use are convenient.
• Time – It reduces time in developing, testing, and launching new products. Aside from that, the extensive network of your provider’s servers ensures that your infrastructure is available for use 24X7.
Disadvantages
• Data and Security Risk – As the name suggests, it’s a public platform for insensitive data storage. As a result of shared resources, security risks are high due to their vulnerability. A user is deprived of knowing where their information is being stored and who all have the access to it.
• Network Performance – Due to an increase in the number of users, the network performance suffers from instability.
• Lack of Customization – Since it’s a public cloud, personalization will always be limited.
Private Cloud Deployment

A private cloud deployment model, also known as an internal or corporate model, is one that belongs to specific organizations. Under this model, the organization is the one that controls the systems and manages them. And while a third party (a service provider) can host a private cloud server, most companies choose to keep their hardware in their on-premises data center from where an in-house team oversees and manages everything. The private cloud deployment model is the second most used model and has it’s own pros and cons which we’ve stated below:
Advantages
• Customization – Unlike the public cloud deployment model, a company using a private cloud can customize its solution as per its own requirements.
• Data and Security – The security of data is high, as in, only authorized internal personnel is allowed to access data. This makes it ideal for storing corporate data. A company can also separate the sets of resources on the same infrastructure which makes it even more secure.
• Control – Your organization is the exclusive owner. You get absolute control over service integrations, IT operations, rules, and user practices.
• Legacy Systems – A special feature about private clouds is that it supports legacy applications that are not functional on public clouds.
Disadvantages
• High Cost – Yes! You’ll need to invest in hardware and software. Aside from that, there are also expenses for in-house staff and training. And not to forget maintenance, which is quite high.
• Limited Scalability – Private clouds are scaled within internal limited hosted resources. Scalability also depends on the choice of your underlying hardware.
Community Cloud Deployment

A community cloud deployment model resembles a private cloud, the only difference being the set of users. While a private cloud implies that one company owns the server, in the case of a community cloud, it is several organizations with similar backgrounds. Companies share the infrastructure and related resources on a community cloud. This model supports joint business organizations, ventures, research organizations, and tenders, etc. Community Cloud is a way to preserve the benefits of economy of scales with the private cloud.
Advantages
• Cost – A community cloud is a cheaper way to avail the benefits of a private cloud. That’s because multiple companies can share the bill together.
• Data Sharing and Collaboration – With a community cloud, sharing data becomes easy and its collaborative space allows clients to enhance their efficiency. Aside from that, configuration and protocols within a community system meet the needs of the specific industry.
Disadvantages
• Limited Storage and Bandwidth– Within community systems, limited storage and bandwidth capacity become a common problem.
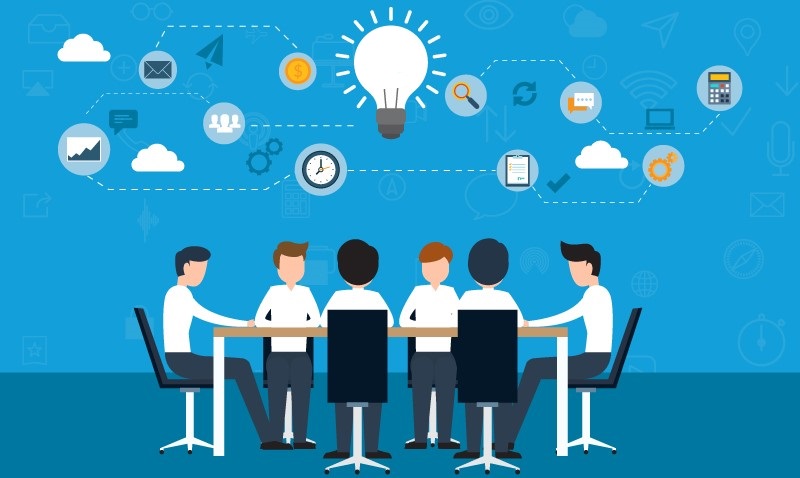
Hybrid Cloud Deployment
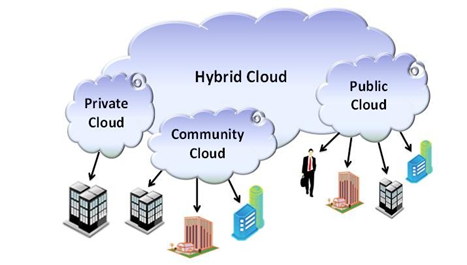
A hybrid cloud deployment model is a combination of two or more cloud servers as one architecture. With a mix of two or more cloud deployment models, organizations are capable of moving data and applications between different clouds, depending on their purpose.
Advantages
• Flexibility and Control – Companies can choose to allocate resources in accordance with specific cases.
• Cost – Since public clouds provide scalability, you’re only liable to pay for the extra capacity and that too in case you need it.
• Agility – In times like today, agility is what brings productivity and progress. With hybrid cloud deployment, your organization will have the opportunity to develop and test new applications in the right period of time.
Disadvantages
• Maintenance– Agree or don’t, a hybrid cloud computing model requires more maintenance which means, a higher operating expense for your organization.
• Challenging Integration – Data and application integration be quite challenging when you’re building a hybrid cloud. It’s also true that activating two or more infrastructures will cover a high initial cost.
For more facts and updates, follow us on Facebook, Twitter, and LinkedIn.